Argentina recorded an increase of 7% in 2024, but it is still below the maximum level of technology adoption.
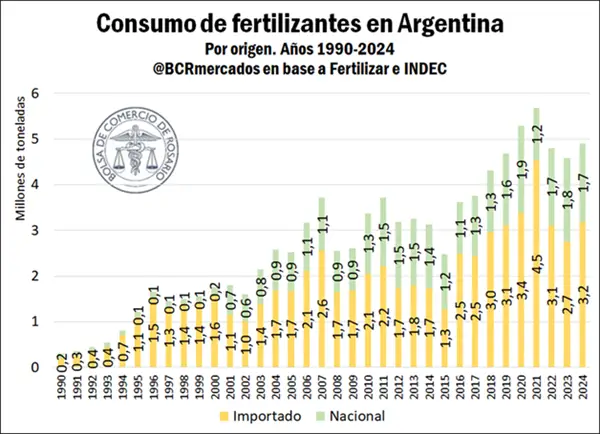
The year 2024 ends on a good note for fertiliser consumption, which has reversed its demand after three years. The increase – according to the Rosario Stock Exchange (BCR) – was 7%.
With plenty of room for growth, 2024 marked the third highest consumption of fertilisers in the country’s history,” said the report, based on data from Fertilizar and the Cámara de la Industria Argentina de Fertilizantes y Agroquímicos (CIAFA).
More fertiliser In 2024, 4.9 million tonnes will be applied. Despite this figure, demand is still below peak consumption levels. In any case, the sector stresses that this is good news because it breaks the downward trend.
The growth in consumption in 2024 is explained by higher soil moisture, the increase in wheat planting and the greater weight of early corn over late corn,” the report says.
The fertilisers that supply the Argentine market are partly domestic and partly imported. In terms of local production, the epicentre of urea supply in the country is Profertil in Bahía Blanca. Other suppliers include Bunge and ACA for phosphate fertilisers.
Imports will account for 65% in 2024. Due to the increase in volume, fertiliser imports totalled US$1,537 million in 2024, 10% more than in 2023.
The main origin of fertiliser imports was Morocco, the world’s main reserve and exporter of phosphate rock and a major player in the world trade of phosphate fertilisers. In addition, Argentina had China as a prominent origin for its monoammonium phosphate imports, ranking second among the country’s main fertiliser suppliers. The United States completes the podium as a major supplier of nitrogen fertilisers,” the BCR said.
In terms of price, fertilisers increased by 13% globally when comparing February 2025 with the same month in 2024. This increase was driven by rising prices for urea, the main imported fertiliser.
Since peaking in February, international urea prices have fallen and are 9% above last year’s levels, as highlighted by Fertiliser Engineering (IF) in one of its recent reports,” the BCR concluded.
Source: Agrofy News.
Kazakhstan is planning to build a $1.3 billion urea plant near the Caspian port Kuryk
Kazakh authorities are set to finalize an agreement within two weeks with Turkish construction firm ESTA Construction for the development of a new fertilizer production plant, as directed by Prime Minister Olzhas Bektenov. The investment in the project is pegged at $1.3 billion.

The plant’s designated site will be located near the port of Kuryk, along the Caspian Sea coast. The facility is expected to produce up to 700,000 tons of urea annually, significantly benefiting Kazakhstan’s agricultural sector by reducing the need to import fertilizers.
Kazakhstan’s fertilizer market
Kazakhstan currently relies heavily on imported mineral fertilizers to support its agro-industrial complex, with annual requirements estimated at 2.5 million tons, predominantly consisting of nitrogen-based products like urea. Russia and Uzbekistan are the primary suppliers at present.
Economic impact
The construction of the new plant is projected to generate approximately 1,000 jobs and sustain about 500 permanent positions post-completion. The initiative is anticipated to spur regional infrastructure development, including enhancements to the Kuryk port, new road constructions, and upgrades to the energy infrastructure. Experts forecast that the plant will contribute over 10 billion tenge in annual tax revenues, bolstering the regional economy significantly.
International collaboration
ESTA Construction was selected for this project due to its extensive experience in large-scale industrial projects across the Middle East and Central Asia, particularly in sectors like oil and gas and chemicals. This collaboration is part of a broader strategy to enhance economic ties between Kazakhstan and Turkey under the bilateral economic partnership plan extending to 2027. Additionally, there are plans to export a portion of the fertilizer produced to neighboring Central Asian countries and China, further expanding the project’s scope.
Source: Fertilizer Daily


ARGENTINA MAIN CROPS OVERVIEW:
SOYBEANS: Rainfall has been recorded over the western strip of the agricultural area and the NEA region. In the latter, these precipitations have not changed the current situation for soybean crops, which continue to show expected yields below average. Nationally, 50 % of first-crop soybeans have already entered the physiological maturity stage. The Core and Córdoba regions are the most advanced and are close to beginning harvest. Meanwhile, in the North-Central Córdoba region, harvesting has started timidly with the first plots, expected to gain pace in the coming days. Around 80 % of second-crop soybeans are between R4 and R5. In the central region, over 80 % of the planted area is in Normal/Excellent condition. Under this scenario, production forecast remains at 48.6 M tons.
CORN: The corn harvest has continued at a steady pace over the past seven days, reaching 19.2 % of the national total, marking a year-on-year advance of 13.2 percentage points. The main factors explaining this progress are a higher proportion of early planting combined with some fields completing their cycle early due to water stress during grain filling. Nationally, the average yield stands at 8.39 Ton/Ha, with the Northern Core zone standing out with an average of 9.64 Ton/Ha. Regarding late-planted corn, all plots are at R3 or later, progressing through this stage with good water availability. However, recent rains in the northern agricultural area are not expected to significantly impact crop conditions in that region. Under this context, the national production forecast remains at 49 M tons.
SUNFLOWER: Regarding sunflower, despite recorded rainfall, the harvest progressed by 19.6 percentage points week-over-week, covering 58.9 % of the suitable area. This progress still reflects a year-on-year delay of -16.1 percentage points but has managed to align with the historical PAS average progress. High yield expectations continue to drive the harvest forward, even in plots where soil conditions are not optimal for machinery access, to prevent additional plant losses and quality issues due to sprouting. Despite varying recorded yields (ranging from 0.8 to 3.8 Ton/Ha), regional averages continue to exceed historical means, which, if maintained in the remaining weeks of harvest, could result in a further increase in the production forecast.
SORGHUM: The grain sorghum harvests advanced by 7.6 percentage points over the last fifteen days and currently covers 16.4 % of the total national area. While several regions are reporting higher-than-expected yields, drought has had a severe impact on the NEA and northern Santa Fe, causing significant production losses. It is important to note that approximately 46.8 % of the total national planted area is concentrated in these zones, meaning production forecasts have been significantly affected. In the NEA, a 37 % yield reduction is estimated, with averages not exceeding 2.0 Ton/Ha. In the North-Central Santa Fe region, although the northern part of the province was as affected as the NEA, some central areas managed to partially mitigate the losses.
Source: Buenos Aires Grain Stock

